Table parts
What are table parts in ClickHouse?
The data from each table in the ClickHouse MergeTree engine family is organized on disk as a collection of immutable data parts.
To illustrate this, we use this table (adapted from the UK property prices dataset) tracking the date, town, street, and price for sold properties in the United Kingdom:
CREATE TABLE uk.uk_price_paid_simple
(
date Date,
town LowCardinality(String),
street LowCardinality(String),
price UInt32
)
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY (town, street);
You can query this table in our ClickHouse SQL Playground.
A data part is created whenever a set of rows is inserted into the table. The following diagram sketches this:
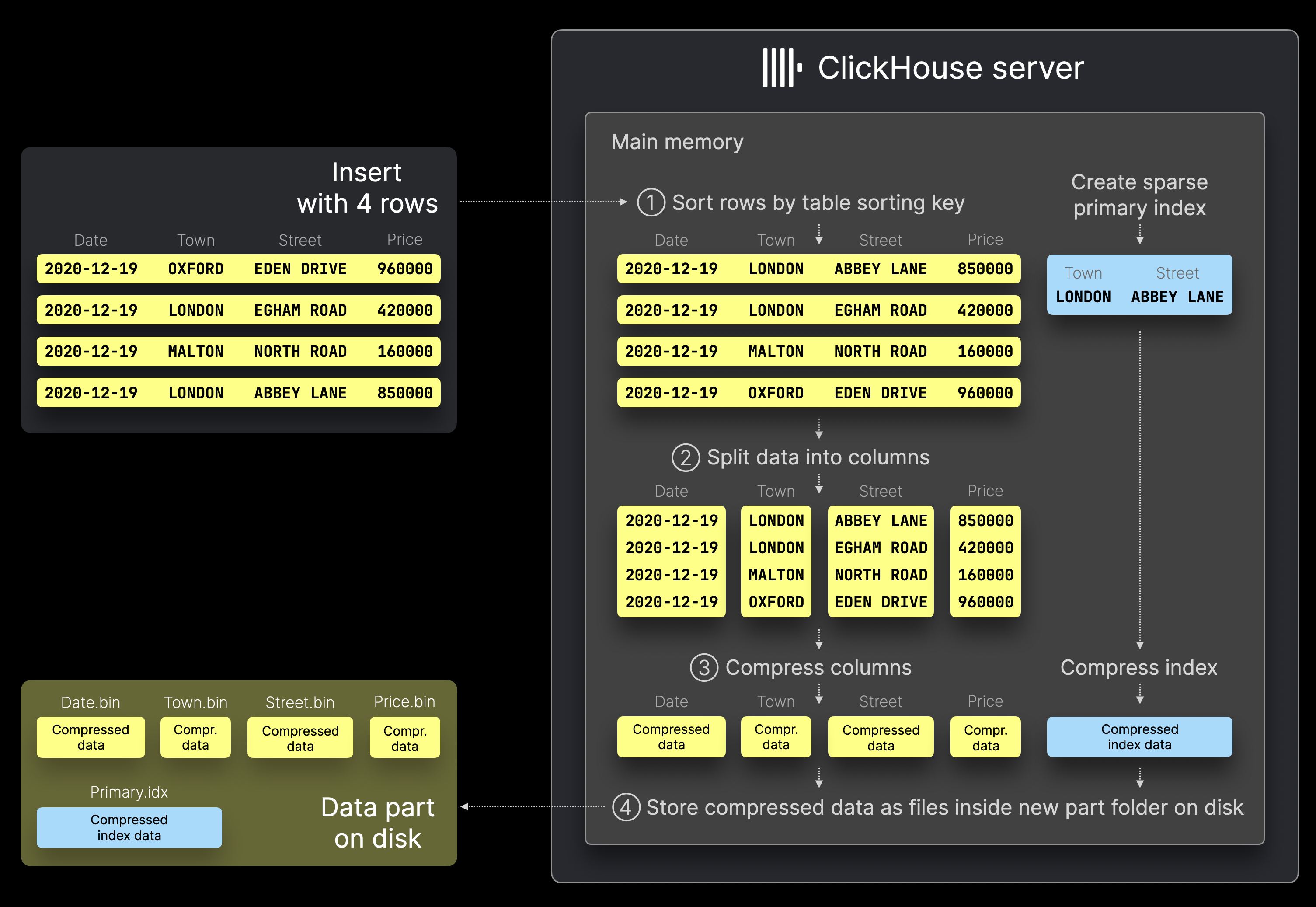
When a ClickHouse server processes the example insert with 4 rows (e.g., via an INSERT INTO statement) sketched in the diagram above, it performs several steps:
① Sorting: The rows are sorted by the table’s sorting key (town, street), and a sparse primary index is generated for the sorted rows.
② Splitting: The sorted data is split into columns.
③ Compression: Each column is compressed.
④ Writing to Disk: The compressed columns are saved as binary column files within a new directory representing the insert’s data part. The sparse primary index is also compressed and stored in the same directory.
Depending on the table’s specific engine, additional transformations may take place alongside sorting.
Data parts are self-contained, including all metadata needed to interpret their contents without requiring a central catalog. Beyond the sparse primary index, parts contain additional metadata, such as secondary data skipping indexes, column statistics, checksums, min-max indexes (if partitioning is used), and more.
To manage the number of parts per table, a background merge job periodically combines smaller parts into larger ones until they reach a configurable compressed size (typically ~150 GB). Merged parts are marked as inactive and deleted after a configurable time interval. Over time, this process creates a hierarchical structure of merged parts, which is why it’s called a MergeTree table:
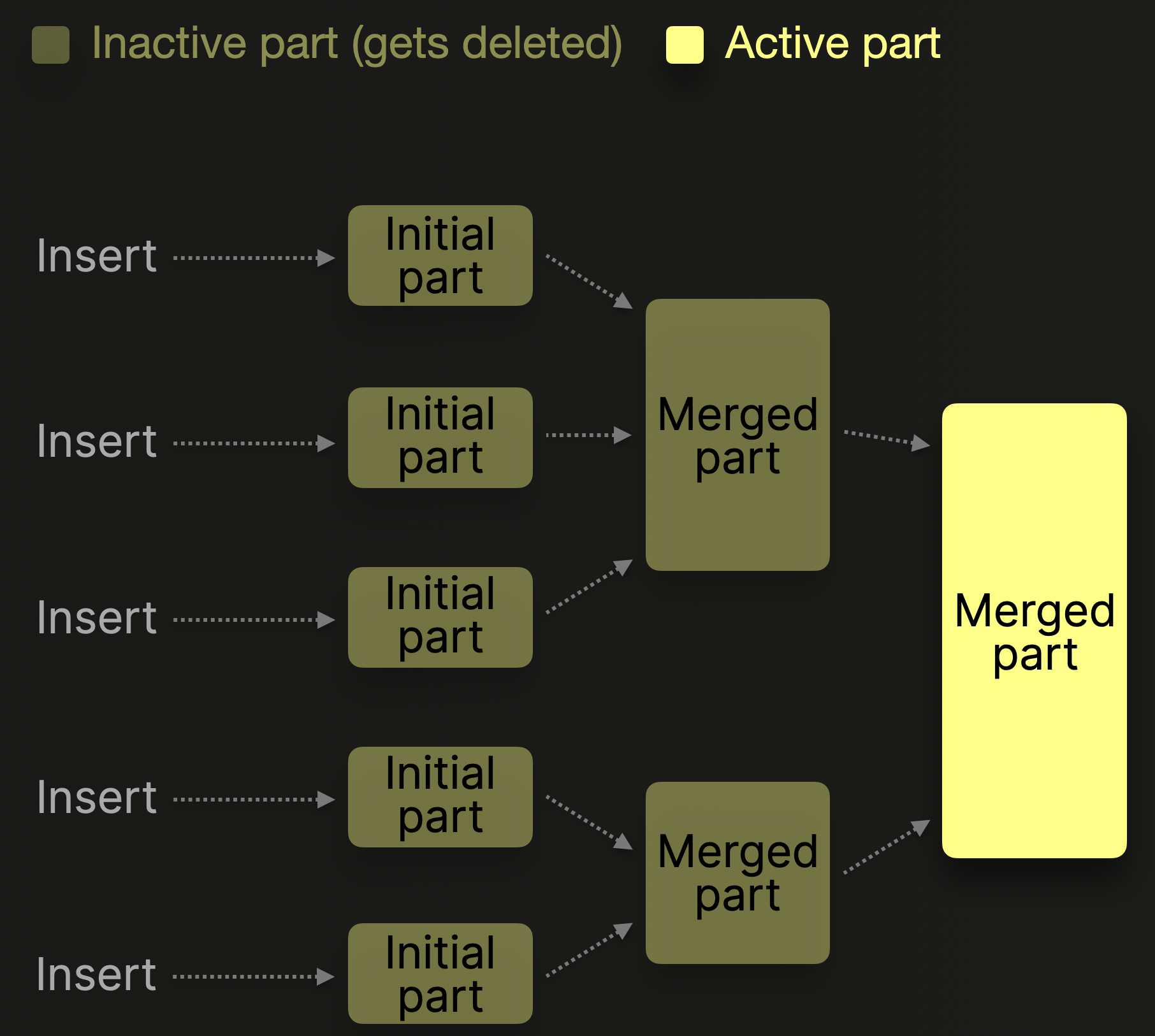
To minimize the number of initial parts and the overhead of merges, database clients are encouraged to either insert tuples in bulk, e.g. 20,000 rows at once, or to use the asynchronous insert mode, in which ClickHouse buffers rows from multiple incoming INSERTs into the same table and creates a new part only after the buffer size exceeds a configurable threshold, or a timeout expires.
You can query the list of all currently existing active parts of our example table by using the virtual column _part:
SELECT _part
FROM uk.uk_price_paid_simple
GROUP BY _part
ORDER BY _part ASC;
┌─_part───────┐
1. │ all_0_5_1 │
2. │ all_12_17_1 │
3. │ all_18_23_1 │
4. │ all_6_11_1 │
└─────────────┘
The query above retrieves the names of directories on disk, with each directory representing an active data part of the table. The components of these directory names have specific meanings, which are documented here for those interested in exploring further.
Alternatively, ClickHouse tracks infos for all parts of all tables in the system.parts system table, and the following query returns for our example table above the list of all currently active parts, their merge level, and the number of rows stored in these parts:
SELECT
name,
level,
rows
FROM system.parts
WHERE (database = 'uk') AND (`table` = 'uk_price_paid_simple') AND active
ORDER BY name ASC;
┌─name────────┬─level─┬────rows─┐
1. │ all_0_5_1 │ 1 │ 6368414 │
2. │ all_12_17_1 │ 1 │ 6442494 │
3. │ all_18_23_1 │ 1 │ 5977762 │
4. │ all_6_11_1 │ 1 │ 6459763 │
└─────────────┴───────┴─────────┘
The merge level is incremented by one with each additional merge on the part. A level of 0 indicates this is a new part that has not been merged yet.